Antioxidants: What They Are and Why You Need Them
Ever wonder why doctors keep talking about antioxidants? In short, they are compounds that protect your cells from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals. When free radicals build up, they can speed up aging and increase the risk of chronic diseases. Antioxidants neutralize those troublemakers, keeping your body running smoother.
Top Natural Sources You Can Grab Today
The easiest way to boost antioxidant intake is through food. Berries – especially blueberries, strawberries and raspberries – are packed with vitamin C and anthocyanins that fight oxidative stress. Leafy greens like spinach and kale bring in lutein and beta‑carotene, while nuts such as almonds and walnuts add vitamin E.
Don’t forget about tea and dark chocolate. A cup of green tea supplies catechins, and a square of 70% cocoa delivers flavonoids that support heart health. If you like cooking, toss tomatoes, bell peppers or sweet potatoes into meals for lycopene and carotenoids.
Choosing Antioxidant Supplements Wisely
Supplements can fill gaps when diet falls short, but not all are created equal. Look for products that list the exact form of the antioxidant – for example, “alpha‑lipoic acid” instead of just “lipoic acid.” Check third‑party testing labels like USP or NSF to ensure purity.
A good rule is to start with a single ingredient supplement rather than a mega‑blend. This makes it easier to see how your body reacts and avoids unnecessary additives. Talk to a pharmacist or doctor if you’re on medication, as some antioxidants can interact with blood thinners or chemotherapy drugs.
Now that you know what antioxidants do, where to find them, and how to pick a safe supplement, it’s time to add them into your daily routine. Start by swapping a sugary snack for a handful of mixed berries, brew green tea instead of soda, and keep a small bottle of vitamin C tablets handy on busy days.
Remember, consistency beats occasional mega‑doses. Your body benefits most from regular, moderate intake rather than a one‑off binge. Pair antioxidants with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and enough sleep for the best protective effect.
If you’re curious about specific antioxidant types – like CoQ10 for heart health or resveratrol for joint support – search our site for those keywords. We’ve got detailed guides that break down dosage, benefits, and possible side effects in plain language.
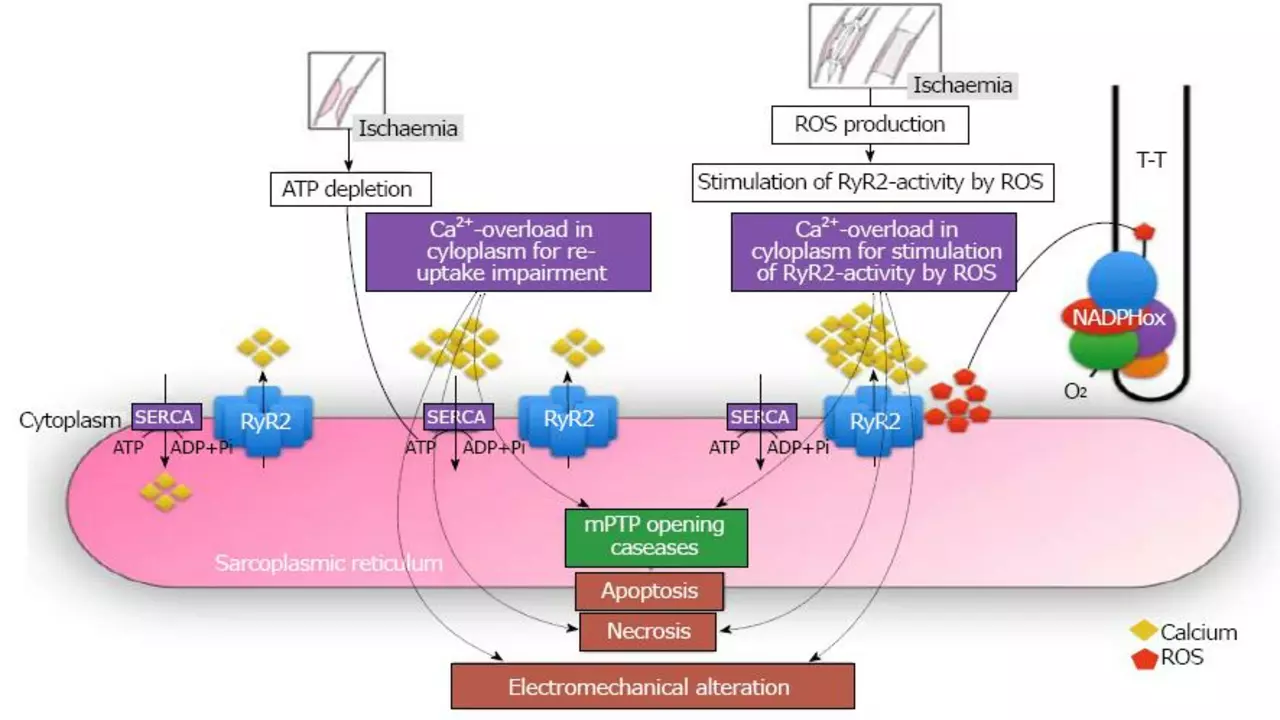
The Role of Antioxidants in Preventing Reperfusion Injury
In my latest exploration, I delved into the critical role antioxidants play in preventing reperfusion injury. This type of injury occurs when blood flow resumes to the tissue after a period of ischemia or lack of oxygen. The sudden oxygen surge can cause significant tissue damage, a process antioxidants help to counteract. These superheroes of the cellular world neutralize harmful free radicals produced during reperfusion, reducing inflammation and cell death. Ultimately, antioxidants play a pivotal role in protecting our bodies during these potentially harmful events.