Understanding Reperfusion Injury
Before we delve into the role of antioxidants in preventing reperfusion injury, it's crucial that we understand what reperfusion injury is. Simply put, reperfusion injury is tissue damage caused when blood supply returns to the tissue after a period of ischemia or lack of oxygen. The absence of oxygen and nutrients from blood during the ischemic period creates a condition in which the restoration of circulation results in inflammation and oxidative damage through the induction of oxidative stress rather than restoration of normal function.
The Importance of Antioxidants
Antioxidants are molecules that can donate an electron to a free radical without making themselves unstable. This ability makes them perfect for stabilizing free radicals and ending the chain reaction before vital molecules are damaged. They play a vital role in maintaining the body's overall health, including the prevention of diseases such as cancer, heart disease, diabetes, and more. Notably, they have been identified to play a significant role in the prevention of reperfusion injury.
Antioxidants and Reperfusion Injury: The Connection
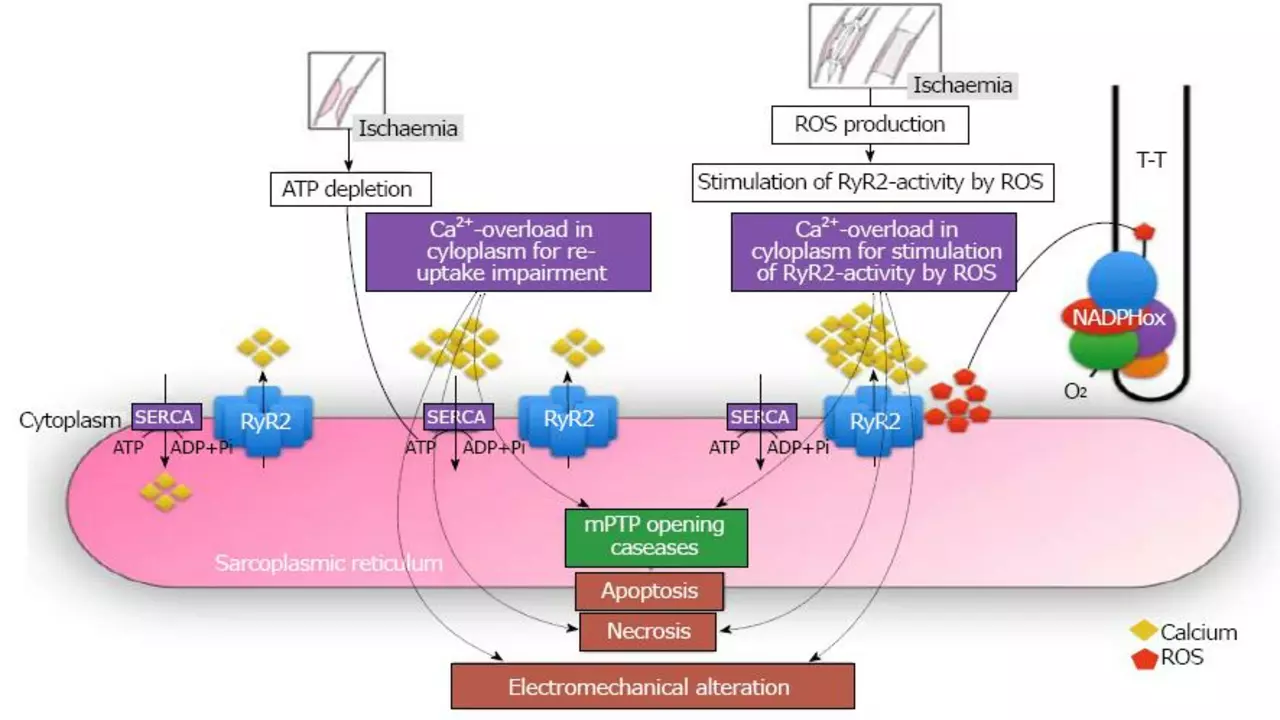
The connection between antioxidants and reperfusion injury lies in the process of oxidative stress. During reperfusion, the sudden influx of oxygen into oxygen-deprived cells leads to a rapid increase in the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), causing oxidative stress. Antioxidants come into play as they neutralize these ROS, thereby reducing the oxidative stress and the resultant damage.
The Role of Vitamin E in Preventing Reperfusion Injury
Vitamin E, a fat-soluble antioxidant, has been shown to have protective effects against reperfusion injury. It works by scavenging free radicals that cause oxidative damage during reperfusion. By including Vitamin E in our diet, we can ensure that sufficient antioxidants are available in our body to counteract the effects of free radicals generated during reperfusion.
The Impact of Vitamin C on Reperfusion Injury
Another crucial antioxidant in the prevention of reperfusion injury is Vitamin C. This water-soluble antioxidant has been identified to reduce the damaging effects of ROS by neutralizing them. In addition, Vitamin C also aids in regenerating Vitamin E, which further enhances the prevention of reperfusion injury.
Other Antioxidants and Their Role in Preventing Reperfusion Injury
Other antioxidants such as glutathione, selenium, carotenoids, and flavonoids also play a significant role in preventing reperfusion injury. They all function in a similar manner, either directly neutralizing free radicals or boosting the body's antioxidant defenses, thereby reducing oxidative stress and preventing reperfusion injury.
Increasing Antioxidant Intake: Diet and Supplements
Given the importance of antioxidants in preventing reperfusion injury, it's essential to ensure that our diet is rich in antioxidants. Foods such as berries, green tea, dark chocolate, and nuts are excellent sources of antioxidants. In addition, antioxidant supplements are also available for those who can't get enough antioxidants from their diet.
Conclusion: The Crucial Role of Antioxidants in Preventing Reperfusion Injury
In conclusion, antioxidants play an indispensable role in preventing reperfusion injury. By neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress, they help prevent the tissue damage associated with reperfusion. Thus, maintaining a diet rich in antioxidants or taking antioxidant supplements is crucial for preventing reperfusion injury. Remember, prevention is always better than cure!
Dylan Kane
July 7, 2023 AT 07:50This whole antioxidant thing is just Big Pharma pushing supplements so they can sell you more junk. You think eating blueberries is gonna save you from a heart attack? LOL.
Yaseen Muhammad
July 7, 2023 AT 21:24While the post presents a scientifically sound overview of antioxidants in reperfusion injury, it omits critical context: many clinical trials on antioxidant supplementation have shown no significant benefit in reducing reperfusion damage in humans. The mechanistic logic is sound, but translation to clinical outcomes remains elusive.
Eben Neppie
July 8, 2023 AT 04:52Let’s be clear - if antioxidants were that effective, we wouldn’t need stents, bypasses, or thrombolytics. The entire premise is reductionist. Oxidative stress is a symptom, not the root cause. Fix the ischemia, not the ROS. This is why so many ‘miracle’ supplements fail in phase III trials.
Sam Tyler
July 8, 2023 AT 23:24It’s important to remember that antioxidants don’t work in isolation. Vitamin C regenerates Vitamin E, glutathione supports enzyme systems, selenium is a cofactor for glutathione peroxidase - it’s a whole network. That’s why popping a single supplement rarely does much. Real protection comes from whole foods: spinach, walnuts, berries, green tea. Your body’s antioxidant system is like an orchestra, not a soloist.
Lugene Blair
July 9, 2023 AT 08:26YES. This is the energy I needed today. You’re not just fighting free radicals - you’re giving your cells a fighting chance. Every bite of dark chocolate, every cup of green tea, it’s a small act of rebellion against chaos. Keep showing up for your body - it’s worth it.
William Cuthbertson
July 10, 2023 AT 00:43There’s a beautiful irony here: the very mechanism that sustains life - oxygen - is also the source of its decay. Reperfusion injury is nature’s paradox. Antioxidants are not a cure, but a gentle reminder that balance, not dominance, is the essence of biological harmony. Perhaps we should not seek to eliminate oxidative stress, but to dance with it - as we have for millions of years.
Steven Shu
July 10, 2023 AT 16:05Agreed with Sam - food first. Supplements are a band-aid. Also, if you’re eating processed crap and then taking vitamin E, you’re just throwing money at a leaky boat.
Cosmas Opurum
July 11, 2023 AT 00:45They don’t want you to know this - but the entire antioxidant narrative is a distraction. Reperfusion injury is being weaponized to sell vitamins while the real cause - corporate greed in hospital protocols - is ignored. Why do ERs still delay reperfusion? Why aren’t antioxidants administered as standard protocol? Ask yourself: who profits from your ignorance?
Shanice Alethia
July 11, 2023 AT 19:15OMG I literally cried reading this. I’ve been taking vitamin C and E since my dad had his heart attack and now I feel like a superhero. Also, I posted this on my Instagram story and 87 people asked where to buy the supplements. I’m basically a medical influencer now 💅
Hudson Owen
July 12, 2023 AT 16:11While the article is well-structured and scientifically accurate, one must consider the limitations of extrapolating in vitro antioxidant mechanisms to in vivo human physiology. The complexity of redox signaling, compartmentalization, and endogenous enzyme systems renders isolated supplementation often ineffective - and in some cases, pro-oxidant.
shridhar shanbhag
July 13, 2023 AT 14:40From India, we’ve known this for centuries - turmeric, neem, amla - these aren’t just spices, they’re medicine. Modern science is just catching up. But don’t forget: traditional diets had variety, not pills. One fruit, one herb, one spice at a time - that’s the real antioxidant stack.
John Dumproff
July 14, 2023 AT 07:14It’s okay if you’re not eating berries every day. What matters is that you care enough to learn. That’s the first step. And if you’re reading this, you’re already doing better than most. Keep going - small changes add up. You’ve got this.
KC Liu
July 14, 2023 AT 13:24So let me get this straight - you’re telling me that a $5 bottle of vitamin E from Walmart can undo decades of arterial plaque buildup caused by Big Ag and Big Pharma’s collusion? I’ve got a bridge in Brooklyn to sell you.